

 Home |
Site Map |
Add to Favorites Link |
Send page to a Friend |
Contact us
Home |
Site Map |
Add to Favorites Link |
Send page to a Friend |
Contact us

|

 Home |
Site Map |
Add to Favorites Link |
Send page to a Friend |
Contact us
Home |
Site Map |
Add to Favorites Link |
Send page to a Friend |
Contact us
|
| About Us | Products | Research and Development | Publications and Press | Clinical Trials | Latest News | Contact us |
 |

10/06/2008
• Listeriosis
The appearance of drug-resistant strains of several pathogens underlies the need for the development of new medicines, including those capable of boosting the host immune response.
This is important in infections by intracellular pathogens since conventional vaccines and antibody-based therapies are often totally or partially ineffective against intracellular pathogens.
The preclinical studies showed that P-MAPA induced proliferation of lymphocyte T, increases cytokine production, NK cell activity and stimulate NO release by macrophages suggesting that P-MAPA may be broadly active, including infections caused by intracellular pathogens.
In view of these findings, the P-MAPA development is also focused on intracellular pathogens in animal models of infections, such as Listeria monocytogenes infected-mice.
Listeria monocytogenes has been widely studied as a model intracellular pathogen to study immunity to infection. Studies have revealed that the T lymphocytes and the cytokines produced play a crucial role in determining the evolution of the host response to bacterial infection.
In this study, we investigated the effects of P-MAPA on the growth and differentiation of bone marrow granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cells (CFU-GM) and citokyne production in Listeria monocytogenes - infected mice.
Results :
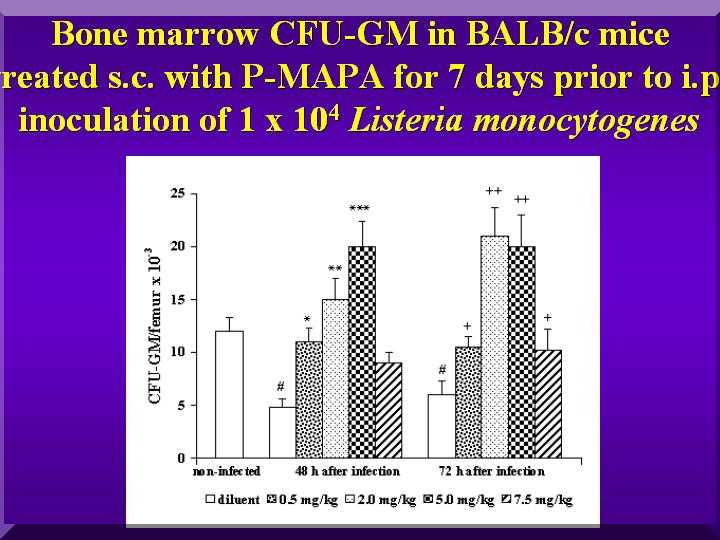
In a first experiment, a significant reduction in the CFU-GM number was observed in the initial phase of infection with a sublethal dose ( 1 x 10 4 cells ) of Listeria monocytogenes.
Treatment of mice with 0,5, 2,5,0 mg/kg and 7,5 mg/kg of P-MAPA for 7 days prior to infection significantly stimulated mylopoiesis in a dose-dependent manner.(Figure 1).
Figure 1
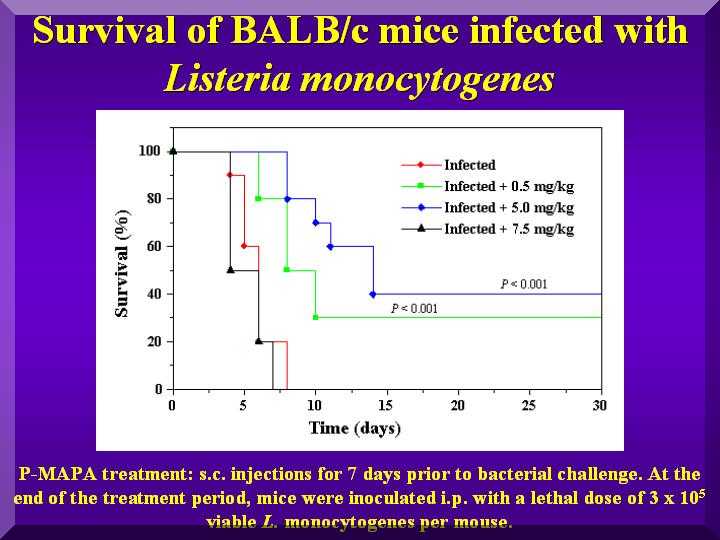
Moreover, in a second experiment, treatment with 0,5 and 5,0 mg/kg P-MAPA resulted in 30% and 40% cures of mice lethally infected ( 3 x 105 cells) with Listeria monocytogenes, respectively (Figure 2).
Figure 2
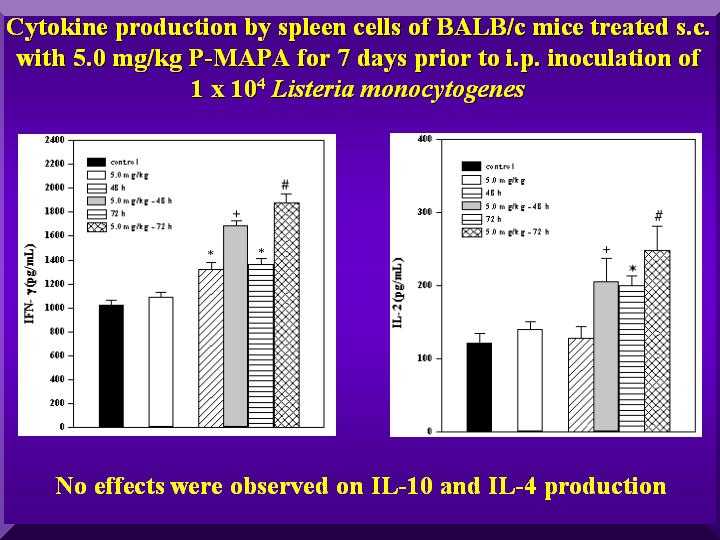
• Effects of P-MAPA on the production of Th1-type and Th2-type cytokines in L. monocytogenes infected mice.
The results suggest a selective up-regulation of antilisterial immunity through enhancement of the Th1-type response since P-MAPA increased IFN-gamma and IL-2 levels 48 h and 72 h after challenge when compared to saline-treated mice. Interleukin-4 and IL-10 production was unaltered by the infection or P-MAPA ( Figure 3).
Figure 3
* Bibliografic references :
A. Melo, G. Z. Justo and M. L. S. Queiroz, "Stimulation of myelopoiesis in Listeria monocytogenes-infected mice by an aggregated polymer isolated from Aspergillus oryzae", Human Exp. Toxicol., 20, 38-45 (2001).
Conclusions
As the ability of hematopoietic tissues to produce phagocytes is of particular significance to mediate resistance to Listeria monocytogenes, the promotion of bone marrow CFU-GM contribute to a rapid restoration of phagocyte numbers in infected sites, thus mitigating the course of infection.
In summary, the experimental data show that P-MAPA can modulated the CFU-GM, cytokine production and bacterial resistance in listeriosis.
The experiments warrant the development of P-MAPA as adjuvant in the treatment of infectious diseases caused by intracellular patogens, increasing the effectiveness of therapies now in use.


|