

 Home |
Site Map |
Add to Favorites Link |
Send page to a Friend |
Contact us
Home |
Site Map |
Add to Favorites Link |
Send page to a Friend |
Contact us

|

 Home |
Site Map |
Add to Favorites Link |
Send page to a Friend |
Contact us
Home |
Site Map |
Add to Favorites Link |
Send page to a Friend |
Contact us
|
| About Us | Products | Research and Development | Publications and Press | Clinical Trials | Latest News | Contact us |
 |

07/10/2008
Effect of P-MAPA on Walker 256- A tumor in Wistar rats
Walker 256 -A tumor: Walker 256-A tumor is known by their growth capacity and lethality after a single subcutaneous (sc) injection in Wistar rats.
Lethality is associated to the severe homeostatic disturbances induced by the W256 -A tumor, which includes anorexia, thymus atrophy and hydro electrolyte disturbances with glomerular filtration and tubular function alterations (Guimarães F.et al, 2010)
Experimental design: two groups of Wistar rats (eight animals each) were inoculated with 4x106 cells Walker 256 A tumor (variant A tumor) and treated subcutaneously with daily doses of 0.5 and 1 mg/kg P-MAPA, beginning 24 h after tumor inoculation. Control animals inoculated with 4x106 cells Walker 256- A tumor (n=8) received only saline.
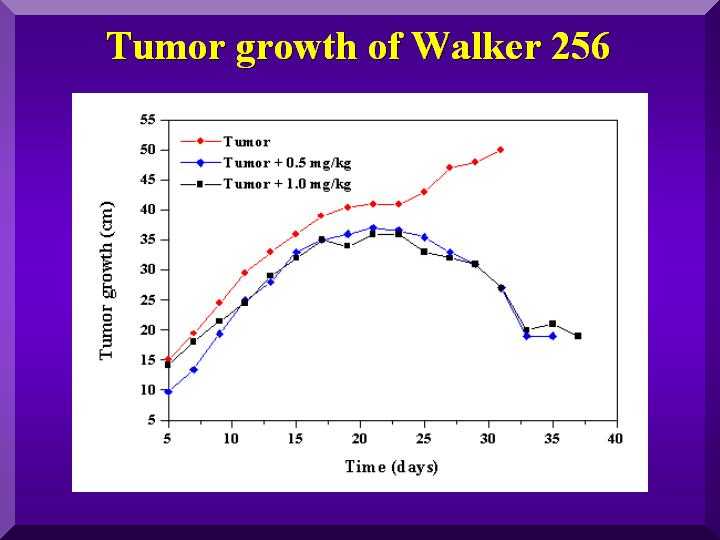
Evaluation of tumoral growth: the development of tumors was evaluated every two days by percutaneous measurements in two dimensions (axial and perpendicular) with a digital caliper. The values in Figure 2 represent the average diameter of tumors of each group of eight animals.
Results: P-MAPA significantly inhibited tumor growth and survival compared with the untreated tumor-bearing animals, which died within 27 days.
In addition, 50% (4/8 animals) and 37.5% (3/8 animals) of animals treated with 0.5 mg/kg and 1 mg/kg with P-MAPA, respectively, exhibited complete tumor regression and enhanced survival rate (Figure 1 and Figure 2).
Of note, mice cured of Walker 256 by MAPA treatment were largely resistant to rechallenge with Walker 256, suggesting a role for T lymphocytes (21).
Figure 1
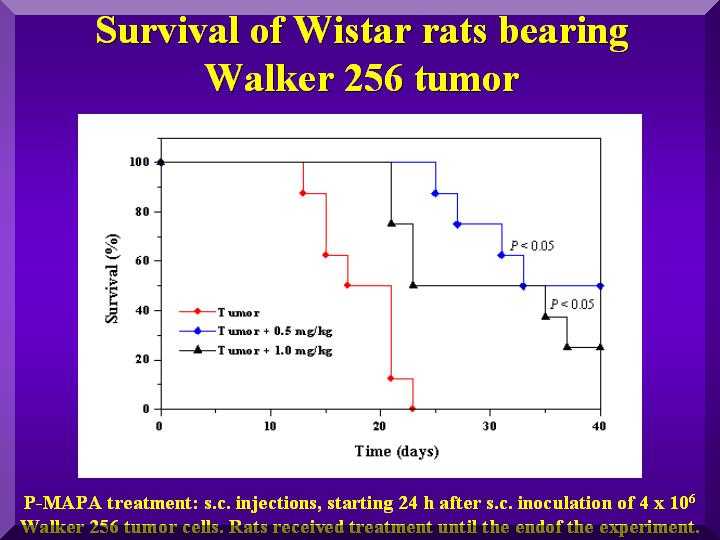
Figure 2
* Published at Int. J. Mol. Med.1999, 4 , S49


|